IJS:将缺乏维生素K或拮抗剂II诱导的蛋白质纳入移植标准扩大了肝细胞癌肝移植的受益者
2023-11-25 Bob Wang MedSci原创 发表于上海
将PIVKA-II纳入现有的LT标准可以增加符合条件的HCC患者的数量,而不会影响LT后的结果。
肝细胞癌(HCC)是世界范围内最具侵袭性和致死性的恶性肿瘤之一,预后差,5年生存率不到20%。在中国,HCC是60岁男性各类癌症中排名第一的死亡原因。HCC治疗的最新进展并没有显著提高患者的生存率。肝移植(LT)仍然是HCC患者的最佳治疗方法。为了避免LT后肿瘤复发,Mazzaferro等人于1996年提出了Milan标准。二十多年来,米兰标准经受住了时间的考验,成为指导肝细胞癌肝移植候选者选择的基准。
尽管米兰标准可以获得良好的长期结果,但近年来由于受体选择的限制,导致HCC患者接受肝移植的机会减少,该标准受到了挑战。理想情况下,这种选择工具应考虑HCC的生物学行为,这是传统影像学检查无法测量的特征。α-胎蛋白(AFP)作为HCC检测的关键生物标志物,反映了HCC的生物学特征,与肝移植后受体的长期生存有关。因此,基于肿瘤大小和术前AFP的选择标准有所改进,如AFP模型和杭州标准。
AFP模型对hcv相关HCC患者肝移植后肿瘤复发的预测效果优于米兰标准,并已被法国肝移植研究小组用于选择肝移植候选者进行器官共享。Xu等人在一项6012例HCC队列的多中心研究中报道,杭州标准预后良好,与米兰标准相比,肝移植适格率提高了51.5%。鉴于HCC的高度异质性,其他生物标志物可以更全面地反映肿瘤进展和恶性程度。
维生素K缺失或拮抗剂- ii (PIVKA-II)是一种凝血活性不足的未成熟凝血酶原,已被广泛应用于临床HCC诊断。PIVKA-II的过量产生预示着包括血管侵袭和HCC转移在内的侵袭性肿瘤行为。因此,监测HCC患者的PIVKA-II可能为制定个性化治疗方案提供有价值的参考。Lee等人证明术前PIVKA-II可用于评估活体供肝移植(LDLT)的预后。然而,由于主流肝移植类型的异质性,这一结论可能不适合中国人群。
在中国,死亡供肝移植(DDLT)是一种比LDLT更常见的HCC手术。以往的研究报道,LDLT比DDLT与更高的肿瘤复发率相关,这影响了结果的稳健性。因此,2023年11月21日发表在International Journal of Surgery的文章,其目的是在一个多中心的中国队列中进一步评估PIVKA-II在受体选择和预后分层中的作用。

本文收集了2015年-2020年在6个中国移植中心接受LT的HCC患者的临床病理数据。进行了单变量和多变量分析,以确定无病生存(DFS)的风险因素。基于这些风险因素,用Kaplan-Meier方法进行了生存分析,并评估了它们在预后分层中的价值。
研究结果显示,共有522名具有LT前PIVKA-II记录的合格HC患者最终被纳入这项研究。肿瘤负担>8厘米,AFP>400纳克/毫升,组织病理学III级和PIVKA-II>240 mAU/mL被确定为DFS的独立危险因素。PIVKA-II≤240 mAU/mL(N=288)患者的DFS明显高于PIVKA-II>240 mAU/mL(N=234)(3-和5年DFS:83.2%、77.3%和75.9%,而75.1%、58.5%和50.5%;P<0.001)。与杭州标准(N=305)相比,将PIVKA-II纳入杭州标准(包括肿瘤负担、AFP、组织病理学等级)使有资格获得LT的患者人数增加了21.6%,但实现了可比的DFS和OS。
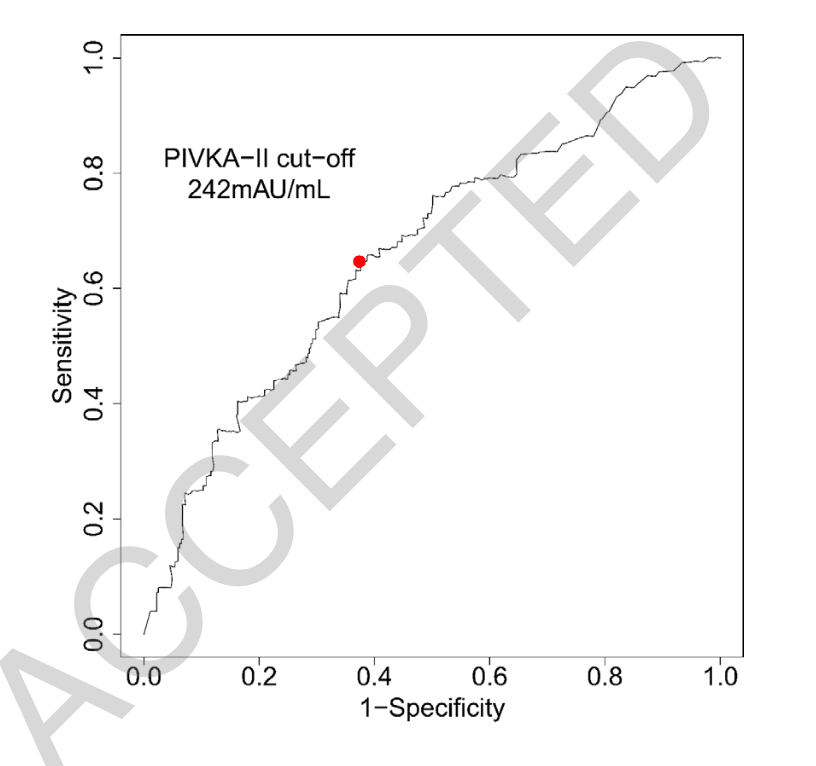
图1:接收器操作特征曲线显示了PIVKA-II肿瘤复发的最佳切点
综上所述,将PIVKA-II纳入杭州标准可以作为一种有效的决策算法,与杭州标准相比,可使符合肝移植条件的HCC患者数量增加21.6%,且不影响肝移植后的预后。因此,HC&PIVKA-II预后分层有望实现中国肝移植学会的建议,并指导肝细胞癌肝移植的临床管理。
原文出处
Wang, Kaia,b,c,d; Dong, Libinb,c,d; Lu, Qiane; Yang, Zhef; Fan, Xiaolig; Gao, Fengqiangb,c,d; Ge, Wenwenb,c,d; Wang, Zhouchengb,c,d; Zhou, Zhishengh; Lu, Dia,b,c,d; Wei, Xuyonga,b,c,d; Wei, Qianga,b,c,d; Zhuang, Lif; Qin, Lunxiui; Ye, Qifag; Yang, Jiayinj; Dong, Jiahonge; Zheng, Shusend,f,k,l; Xu, Xiaob,c,d,h. Incorporation of protein induced by vitamin K absence or antagonist-II into transplant criteria expands beneficiaries of liver transplantation for hepatocellular carcinoma: A multi-center retrospective cohort study in China. International Journal of Surgery ():10.1097/JS9.0000000000000729, November 21, 2023. | DOI: 10.1097/JS9.0000000000000729
本网站所有内容来源注明为“梅斯医学”或“MedSci原创”的文字、图片和音视频资料,版权均属于梅斯医学所有。非经授权,任何媒体、网站或个人不得转载,授权转载时须注明来源为“梅斯医学”。其它来源的文章系转载文章,或“梅斯号”自媒体发布的文章,仅系出于传递更多信息之目的,本站仅负责审核内容合规,其内容不代表本站立场,本站不负责内容的准确性和版权。如果存在侵权、或不希望被转载的媒体或个人可与我们联系,我们将立即进行删除处理。
在此留言















签到学习
27
#ijs#不错不错
27
#肝细胞癌# #维生素K# #拮抗剂II#
39