J Food Sci:芦笋或可助缓解宿醉痛苦
2013-01-06 J Food Sci 搜狐科学 尚力
宿醉是因过量饮酒导致的醉酒后状态,会伴随头痛、口渴、眩晕、胃病、恶心、呕吐、失眠、手颤和血压升高或降低等症状,带给人的痛苦不言而喻。美国食品科技学会(Institute of Food Technologists)在《食品科学》(Journal of Food Science)杂志上刊登了一份有关如何缓解宿醉痛苦的研究报告,报告称,芦笋提取物中发现的氨基酸和矿物质或能缓解宿醉痛苦,保护肝细胞免受毒
宿醉是因过量饮酒导致的醉酒后状态,会伴随头痛、口渴、眩晕、胃病、恶心、呕吐、失眠、手颤和血压升高或降低等症状,带给人的痛苦不言而喻。美国食品科技学会(Institute of Food Technologists)在《食品科学》(Journal of Food Science)杂志上刊登了一份有关如何缓解宿醉痛苦的研究报告,报告称,芦笋提取物中发现的氨基酸和矿物质或能缓解宿醉痛苦,保护肝细胞免受毒素侵害。
医学科学协会(Institute of Medical Science)和韩国济州国立大学(eju National University)的研究人员分析了芦笋嫩枝和叶子的成分,并将其作用于人体肝细胞的生物化学反应和作用于鼠肝细胞的生物化学反应进行了对比。首席研究员金姆(B.Y. Kim)表示:“叶子中发现的氨基酸和矿物质含量比嫩枝中发现的多。”
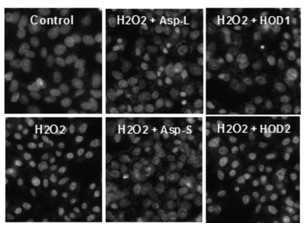
长期服用酒精会对肝造成氧化压力,并给人带来与宿醉有关的身体反应,如头痛、恶心等。金姆称:“让宿醉人士服用芦笋叶子和嫩枝提取物,我们发现其细胞毒性明显降低,这个结果为‘芦笋的生物学功能如何帮助减轻宿醉痛苦和保护肝细胞’提供了依据。”
芦笋是一种非常普遍的蔬菜,在全球各地都能买到。由于其独特的抗癌作用,芦笋一直被当作草药使用。除了抗癌外,它还有抗真菌、抗发炎和利尿的作用。

Effects of Asparagus officinalis Extracts on Liver Cell Toxicity and Ethanol Metabolism
本网站所有内容来源注明为“梅斯医学”或“MedSci原创”的文字、图片和音视频资料,版权均属于梅斯医学所有。非经授权,任何媒体、网站或个人不得转载,授权转载时须注明来源为“梅斯医学”。其它来源的文章系转载文章,或“梅斯号”自媒体发布的文章,仅系出于传递更多信息之目的,本站仅负责审核内容合规,其内容不代表本站立场,本站不负责内容的准确性和版权。如果存在侵权、或不希望被转载的媒体或个人可与我们联系,我们将立即进行删除处理。
在此留言








#food#
41